CA Director General Francis Wangusi says this will focus on putting support physical infrastructure, a project that is expected to take one year/FILE
NAIROBI, Kenya, Apr 5 – The Communications Authority of Kenya (CA) plans to spend at least Sh1.5 billion from September to put the missing ICT infrastructure across the country.
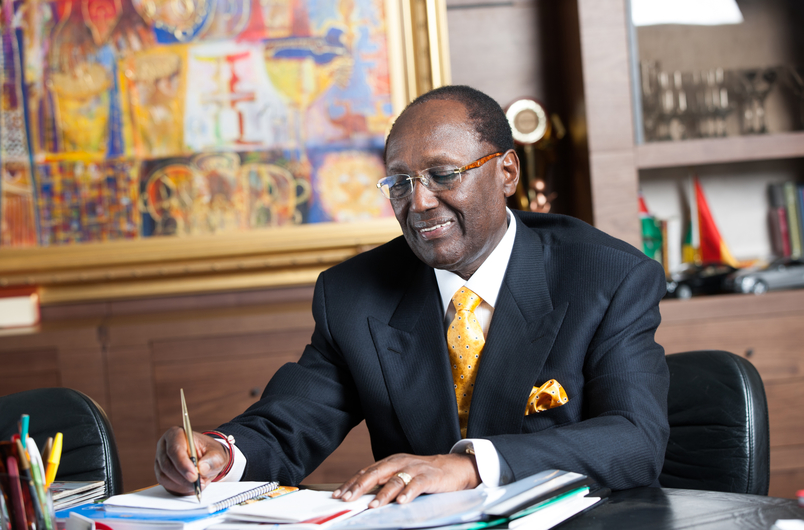
CA Director General Francis Wangusi says this will focus on putting support physical infrastructure, a project that is expected to take one year.
“We want the first implementation to start from September 2016. Already, we have set aside a budget of Sh1.5 billion which will be used to connect the gaps in the ICT infrastructure, as well as connect broadband to some schools, that will be identified in the counties,” Wangusi said.
Some of the projects will include building of base stations, rolling out of more optic fibre as well as other putting physical infrastructure that will allow all ICT connectivity to be done.
Wangusi was speaking on Tuesday during the release of the ICT Access Gap Study Report.
The study is aimed at conducting a country level assessment to determine the extent of communication coverage and the access levels by citizens in the telecommunications, post and courier and broadcasting sectors, and the gaps in infrastructure and service coverage across all sub-locations in Kenya.
On basic mobile voice service gap, at least 164 sub-locations, mainly in the North Rift and North Eastern regions of the county remain with zero coverage with another 414 sub-locations having less than 50 percent population coverage.
“The basic mobile voice service gap has reduced to 5.6 percent of the population which is a major achievement as the gap was still 11 percent of the population in 2011. This is largely due to expansion by the commercial operators, market forces and a well-regulated competitive sector,” the study by Intelecon Research and Consultancy Company explains.
The report proposes a large contribution to closure of the remaining gap in basic voice services which will help will reduce the population coverage gap from 5.6 percent of the population to 2.8 percent by 2018.
On courier services almost all constituencies (264 out of 295) have at least one post office, and a third of the wards have a post office. However, access standards for universal postal services are yet to be developed by policymakers, based on actual demand.
On broadcasting, at least 60 percent of the population is covered by Digital Terrestrial Television (DTT) through the two licensed signal distributors KBC – Signet and Pan African Group (PANG).
However the most recent TV penetration estimate noted in this report indicated that only 32 percent of Kenyan households own a TV.
If ICT infrastructure is put beginning September, “all counties will have at least one transmitter and more than 47percent of sub-locations will have greater than 90 percent signal coverage. Another 12 percent will have better than 50 percent coverage. 1,927 sub-locations will still remain without any coverage.”
Intelecon Research and Consultancy Limited was contracted by CA in November last year to conduct the study which will inform part of the implementation of Universal Service Fund (USF) programmes.
The USF was created through the Kenya Information Communication Act to be supported by operators through contribution of 0.5 percent of the gross turnover.